Thyroid
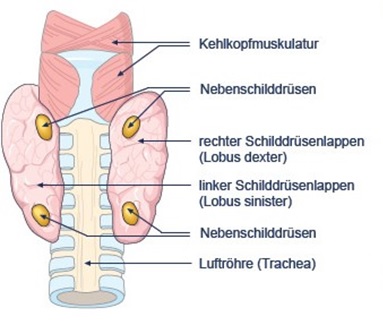
The thyroid is a relatively small organ, lying against and around the larynx and trachea. Female thyroid glands weigh up to 18 g, male ones up to 25 g.
more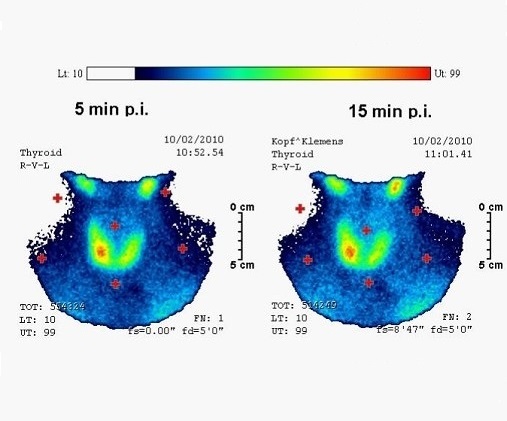
Parathyroid gland
The parathyroid glands are two pairs of glands having the size of apple seeds usually positioned behind the left and right lobes of the thyroid
more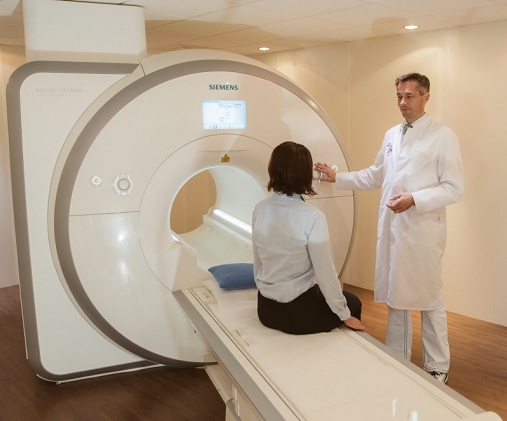
PET/CT and MRI
This imaging techniques belong to the most accurate modalities in the field of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine..
more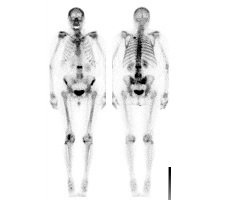
Skeleton/bones
The skeletal scintigraphy or bone scan is the most sensitive method for the presentation of bone metabolism.
more
Heart
With myocardial scintigraphy the perfusion (blood flow) of the heart can be measured at rest and during exercise by the use of radioactively marked substances.
more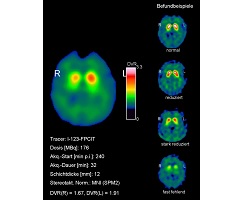
Brain
It is increasingly clear that Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases present a challenge for our society.
more